Renal problems occur three times more frequently in cats than dogs but most do not show signs of chronic kidney disease until 75% of the kidneys have been damaged.
Conditions
Renal disease, also referred to as kidney disease or failure occurs in both cats and dogs.
Hypocalcaemia is a condition in which the calcium level in the blood is too low. It is also known as eclampsia or milk fever.
Hyperthyroidism is the most common endocrine (hormonal) disorder of cats. It most commonly affects older cats and is caused by an increase in the production of thyroid hormones from the thyroid glands in the neck.
When a pet is exposed to high temperatures either by being left in the sun without any shade or being locked in a car on a warm day heatstroke or hyperthermia can occur. If dogs are too hot and are unable to reduce their body temperature by panting, they will develop heatstroke which can kill.
FLUTD is the name used for a collection of common conditions affecting the cat’s bladder and/or urethra. The urethra is the narrow tube which carries urine from the bladder to the outside. Included in this description is cystitis (inflammation of the bladder).
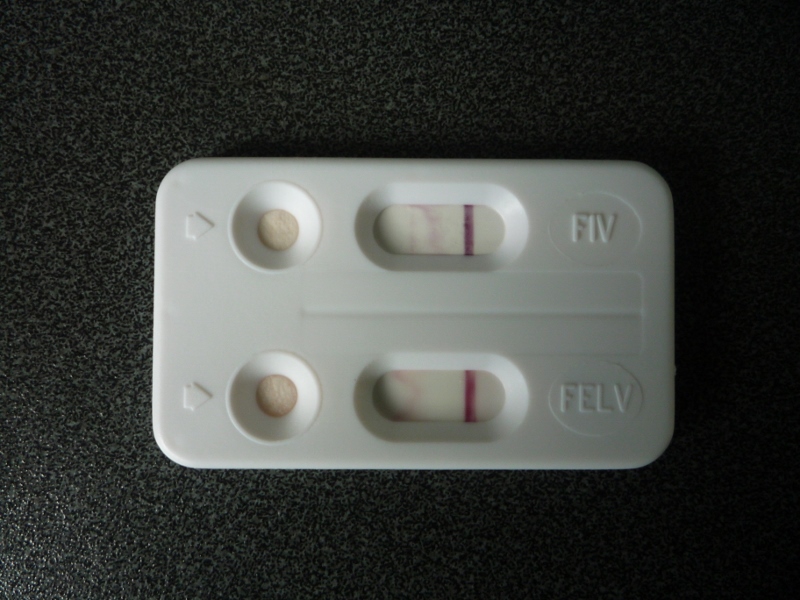
Feline Leukaemia Virus is a viral infection of cats which is common in stray and unvaccinated cats. The virus infects immune system cells (white blood cells) leaving the cat vulnerable to secondary infections which would not be a problem in normal, healthy cats.
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) affects cells of the immune system (white blood cells) causing a gradual decline in the cat’s immune function. As the immune system is vital in fighting infections, infected cats are at a very high risk of disease and infection.
Page 2 of 4